2121. Find if Path Exists in Graph
Easy
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex ui and vertex vi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex source to vertex destination.
Given edges and the integers n, source, and destination, return true if there is a valid path from source to destination, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
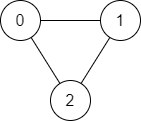
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
Output: true
Explanation: There are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
Example 2:
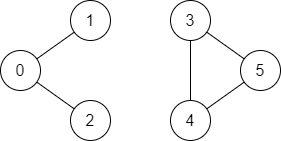
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1- There are no duplicate edges.
- There are no self edges.
<내코드>
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
if source == destination : return True
# 2. DFS 사용
def dfs(graph, start_node, end_node):
# DFS 위한 스택과 방문관련 set선언
stack = deque()
visited = set()
stack.append(start_node)
visited.add(start_node)
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
for val in graph[node]:
# 이미 방문했는지 체크
if val in visited:
continue
# 목적지인지 체크
if val == end_node:
return True
stack.append(val)
visited.add(val)
return False
# 1. 인접리스트 만들기
adj_list = {i : [] for i in range(n)}
for u,v in edges:
adj_list[u].append(v)
adj_list[v].append(u)
print(adj_list)
return dfs(adj_list, source, destination)
- 2가지의 큰 과제
1. 인접리스트 구현하기
2. DFS 구현하기
=> 인접리스트는 예시를 보고 사실상 따라서 만들었고, DFS는 명세를 보고 하나씩 참고해서 만들었음
=> 생각할수록 뿌듯함
- 인접리스트 구현 시 딕셔너리에 대한 컴프리핸션도 가능함
=> 특히 양방향 그래프이므로 양쪽에 append를 해주면 됨
- 방문여부는 어렵게 접근하기보다는 set()으로 쉽게 가능함
- stack 은 deque 보다 일반 list로 해도 쉽게 이용이 가능함
<모범사례>
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
if source == destination:
return True
adj_list = {i: [] for i in range(n)}
for u, v in edges:
adj_list[u].append(v)
adj_list[v].append(u)
queue = deque([source])
visited = set([source])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node == destination:
return True
for neighbor in adj_list[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
visited.add(neighbor)
queue.append(neighbor)
return False
<보충학습>
1. DFS와 BFS 접근방향 차이
DFS : stack, recursive 로 구현 / 특정 경로가 존재하는지 확인
BFS : queue 로 구현 / 최단경로가 존재하는지 확인
- 본 문제는 출발지에서 부터 목적지까지 경로가 있는지 이므로 DFS가 바람직한것으로 파악이 됨
2. 실무 활용 예
- 네트워크 분석(노드 간 관계를 찾거나 경로 분석시)
- 지도 및 네비게이션 (최단경로를 찾거나 특정지점간 연결성 찾기위해)
- 의존성 관리 (모듈 간 의존성 관리할 때)
'문제풀이 > 일일연습문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [practice]99클럽 코테 스터디 25일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/1/172928. 공원 산책 (0) | 2024.08.17 |
|---|---|
| [practice]99클럽 코테 스터디 24일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/1/161990. 바탕화면 정리 (0) | 2024.08.16 |
| [Graph]99클럽 코테 스터디 22일차 TIL + 1916-find-center-of-star-graph (0) | 2024.08.15 |
| [Greedy]99클럽 코테 스터디 21일차 TIL + 0561-array-partition (0) | 2024.08.14 |
| [DP]99클럽 코테 스터디 20일차 TIL + 0119-pascals-triangle-ii (0) | 2024.08.13 |