1651. Shuffle String
Easy
You are given a string s and an integer array indices of the same length. The string s will be shuffled such that the character at the ith position moves to indices[i] in the shuffled string.
Return the shuffled string.
Example 1:
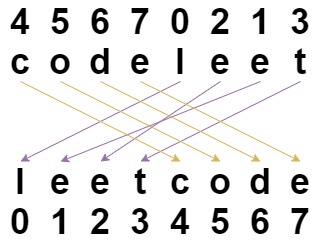
Input: s = "codeleet", indices = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3] Output: "leetcode" Explanation: As shown, "codeleet" becomes "leetcode" after shuffling.Example 2:
Input: s = "abc", indices = [0,1,2] Output: "abc" Explanation: After shuffling, each character remains in its position.
Constraints:
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100sconsists of only lowercase English letters.0 <= indices[i] < n- All values of
indicesare unique.
<코드>
class Solution:
def restoreString(self, s: str, indices: List[int]) -> str:
t = [0 for i in range(len(s))]
for i in range(len(s)):
t[indices[i]] = s[i]
return ''.join(t)- 여기서 특정 길이만큼 배열을 0으로 초기화 하는 방법을 배우게 됨
- 복잡하게 append(), insert() 를 생각할 필요없이 이미 자리한 배열에다가 그대로 대입하면 쉽게 가능함
- 마지막 각 문자열배열을 하나의 문자열로 쉽게 합쳤음
<배운점 및 반성>
class Solution:
def restoreString(self, s: str, indices: List[int]) -> str:
resp = ["0"] * len(indices)
for i, s in zip(indices, s):
resp[i] = s
return "".join(resp)
# temp = dict(zip(indices, s))
# return "".join(map(lambda x: temp[x], range(len(indices))))- 다음 코드 처럼 zip을 이용할 수 있다는것일 잊어버림
'문제풀이 > 일일연습문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 99클럽 코테 스터디 2일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/1/12944. 평균 구하기 (0) | 2024.07.23 |
|---|---|
| 99클럽 코테 스터디 1일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/1/12932. 자연수 뒤집어 배열로 만들기 (1) | 2024.07.22 |
| 99클럽 코테 스터디 13일차 TIL + 1572-subrectangle-queries/ (0) | 2024.06.14 |
| 99클럽 코테 스터디 12일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/3/43238. 입국심사 (1) | 2024.06.11 |
| 99클럽 코테 스터디 11일차 TIL + 프로그래머스/2/43165. 타겟 넘버 (0) | 2024.05.31 |